
The future of drug therapy
Pharmacogenetics (PGx)
Every human being is unique – and their response to medication is just as individual. Pharmacogenetics investigates how our genes influence the effect of drugs.
This knowledge enables personalized medication, whereby the right medication in the appropriate dosage can be selected for each individual patient. This makes therapies more effective and reduces side effects.
Explanation
Our genetics effect the efficacy and safety of medications
Genetic differences among patients are mostly not taken into account in today’s (one-size-fits-all) drug therapy.
Therefore, it is common for a medication to have the desired therapeutic effect for one patient, while for another patient, it may lead to treatment failure or adverse drug reactions (ADR).
PHARMACOGENETICS
effect of medication taking genetic characteristics into account
What is pharmacogenetics?
Pharmacogenetics (PGx) investigates the influence of different genetic variants in a patient on the metabolism of drugs.
How do genetic variants influence the effect of drugs?
Enzymes, transport proteins, and receptors regulate the absorption, distribution, and excretion of drugs in the body. Genetic differences influence both their quantity and function, and thus the speed at which drugs take effect and are broken down.
Since when has pharmacogenetics existed?
The term pharmacogenetics was coined in 1959 by Friedrich Vogel, who laid the foundation for a new field of research and personalized medication.

What is analysed in pharmacogenetics?
A pharmacogenetic test examines selected genes for variants that effect the metabolism of specific medications.
Pharmacogenetics enables Personalized Medication
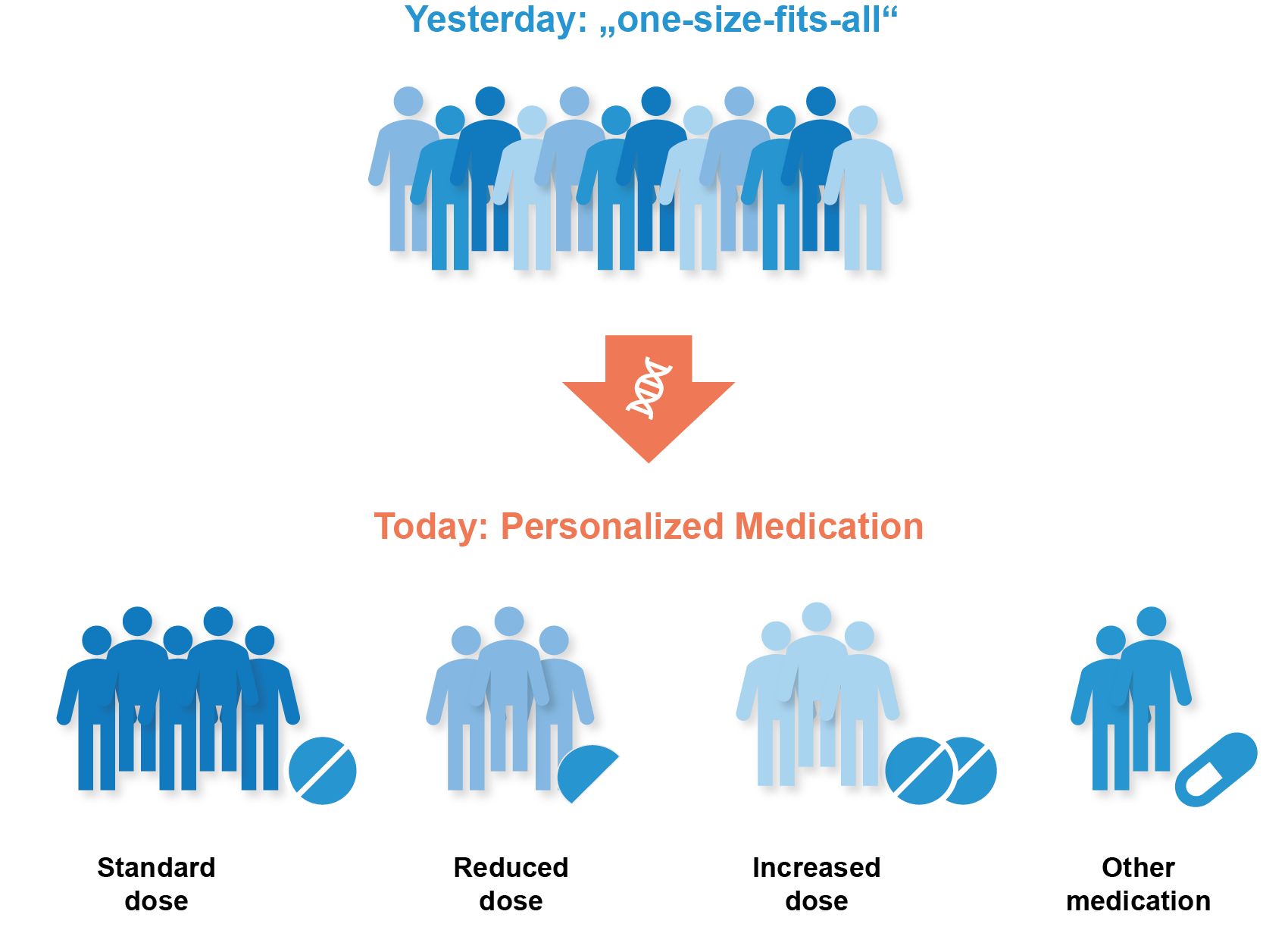
individualization
How does PGx support physician?
The results of a patient’s pharmacogenetic test can be used to individually adjust the selection and dosage of medication.
This allows risks to be avoided before taking a drug or to diagnose and reduce side effects that have already occurred. This complements existing diagnostic procedures as a decision-making aid and pursues the approach of personalized medicine.
In which medical indications does pharmacogenetics play a role?
Pharmacogenetics plays an important role in a wide range of clinical conditions. The PGXperts system contains evidence-based data on more than 150 drugs that are influenced by genetics (gene-drug pairs) and can be used for various indications.
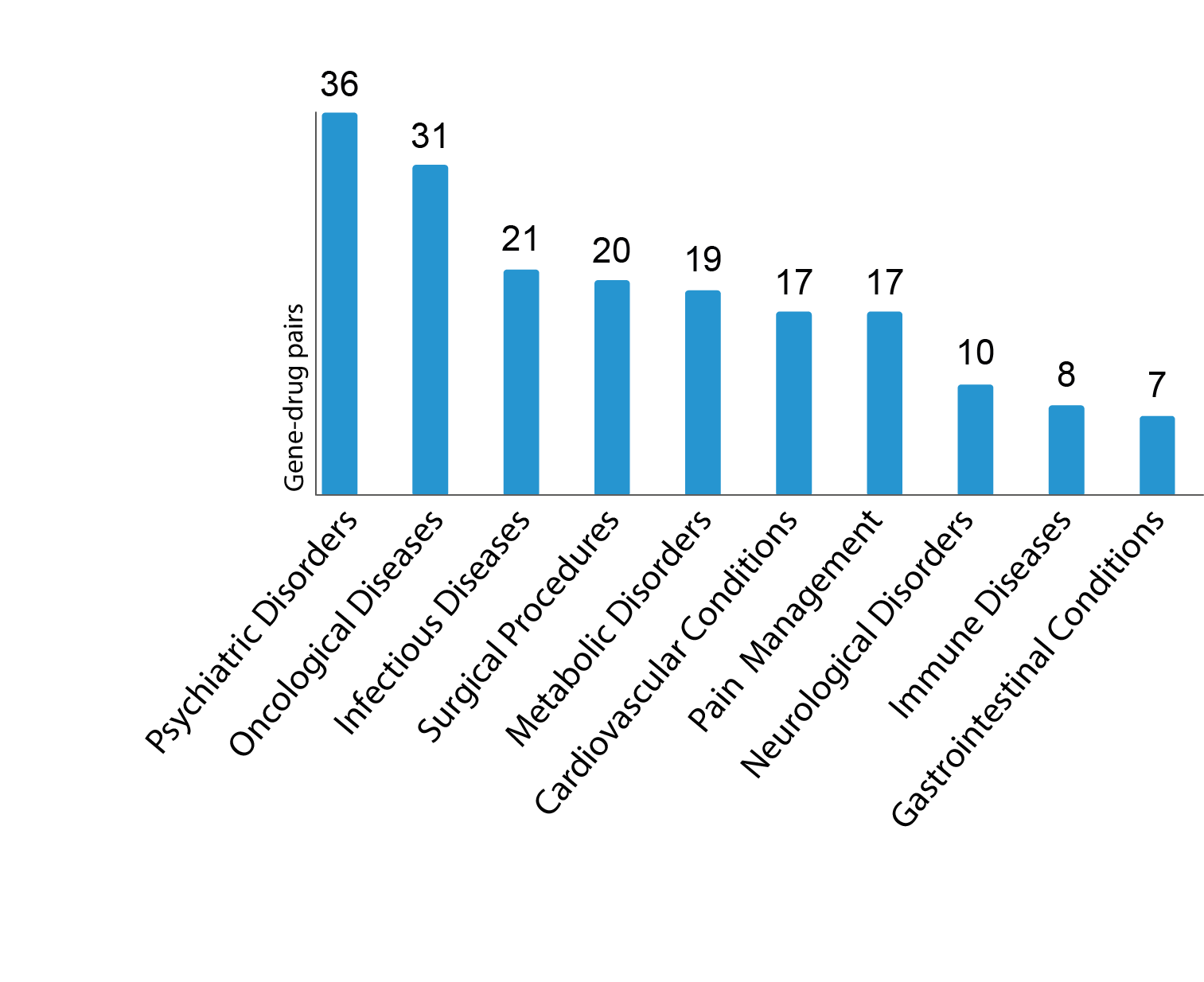
%
of the population can benefit from pharmacogenetics
Genetic occurrence
Personalized medication for everyone
A US study involving over 10,000 participants showed that 99% of people have at least one genetically relevant variant that can influence the efficacy or compatibility of medications.
What types of metabolization are there?
Pharmacogenetics distinguishes between several metabolization types in order to describe the speed of a patient’s metabolism for a specific drug.
Slow metabolism (poor metabolizer) leads to excessive drug concentrations and can cause serious side effects.
In the case of intermediate metabolizers(intermediate metabolizer) the duration of action is prolonged, and side effects are more likely.

Personalized Medication
offers numerous benefits
Increased therapeutic success
Increased response rate and reduced risk of adverse drug reactions
Reduction of costs
Reduction of direct and indirect treatment costs
Early detection
Identifying risks of complex medications before treatment
Lifelong benefits for patients
One-time examination for a patient & lifelong benefits through personalized medication
Relief for medical professionals
Fewer hospital admissions and doctor visits due to side effects and medication errors
PGx testing
Pharmacogenetic testing for clinics and medical practices
With a PGx test from PGXperts, doctors can take their patients’ genetic predispositions into account—for safe, effective, and personalized medication.

Since when has pharmacogenetics existed?
The origins of research into individual drug response date back to the 1950s, when genetic variations were first identified as the cause of differences in drug processing. The term was coined in 1959 by Friedrich Vogel, who laid the foundation for a new field of research.
The decoding of the genome in 2003 was a milestone for personalized medicine. Technological advances and reduced costs in gene analysis and data processing now make it possible to incorporate evidence-based research findings into decisions on medication.
Natural changes in the DNA sequence, known as polymorphisms, are passed down from parents to offspring. These genetic variants can effect gene function (genotype) and can change both external traits, such as eye and hair color, as well as biological processes (phenotypes).
What is analysed in pharmacogenetics?
A pharmacogenetic analysis is carried out using DNA obtained from either a blood or saliva sample. Specific sections of the DNA are examined for genetic variants, known as SNPs (single nucleotide polymorphisms), which, based on extensive research, are known to influence the metabolism of certain medications.
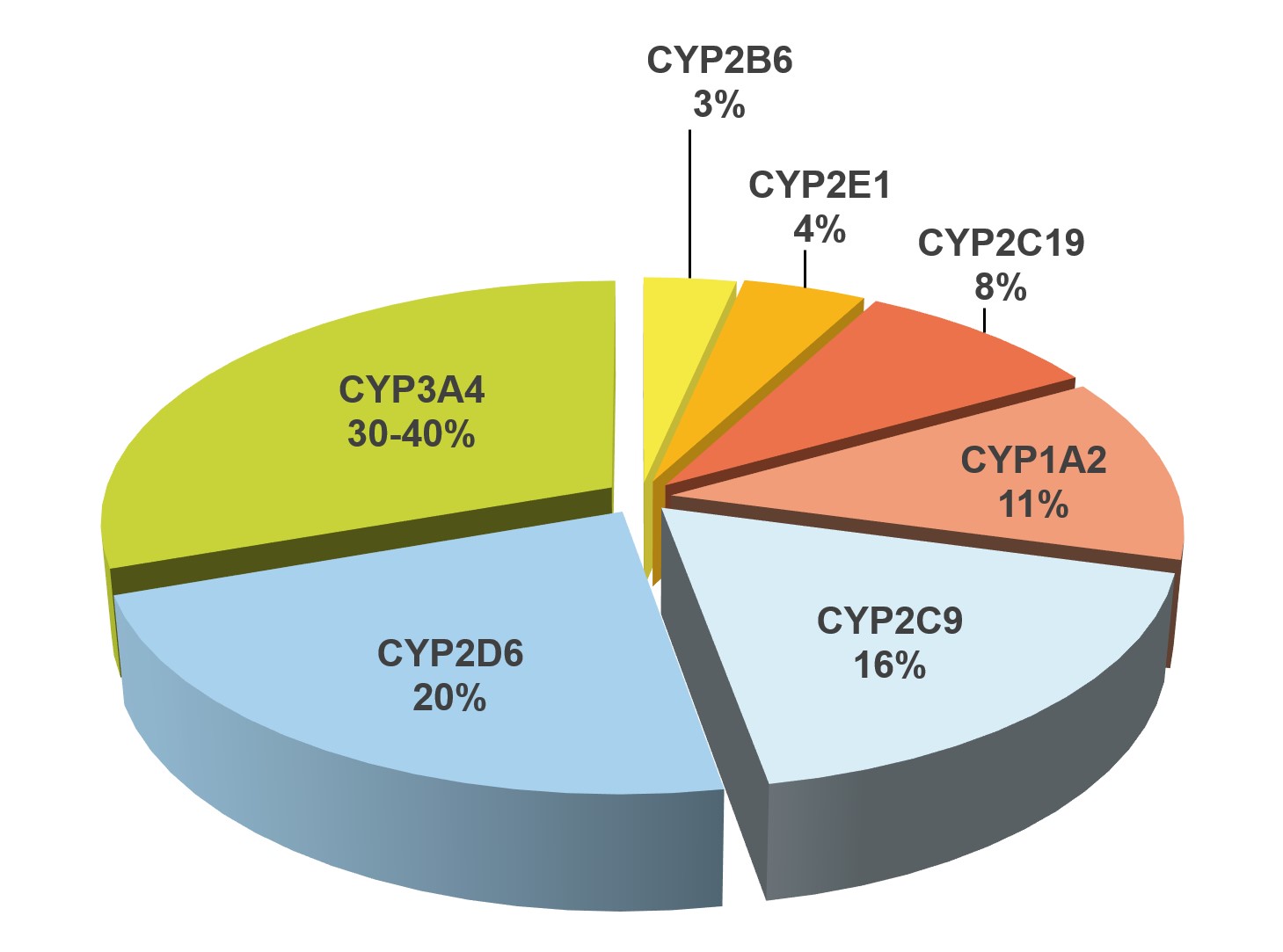
The metabolism of most drugs is catalyzed by enzymes of the cytochrome P450 (CYP) system. The differences in the function of these CYP450 enzymes are the reason why the intensity and duration of effects and side effects can vary greatly from patient to patient for the same dosage of a drug.
From a clinical point of view, CYP2B6, CYP2D6, CYP2C19, CYP2C9, CYP3A4 and CYP3A5 are particularly relevant, as they metabolize between 70 and 90% of the drugs used *.

